When a software is composed of different layers, friction occurs. That’s when features turn into bugs.
 There is a strong urge to make software smart. Whenever something smart gets built in, it’s called a feature. Features of a software are effects you don’t foresee, but find handy for your use case. If your use case is impaired by a feature, you’ll likely call it a bug.
There is a strong urge to make software smart. Whenever something smart gets built in, it’s called a feature. Features of a software are effects you don’t foresee, but find handy for your use case. If your use case is impaired by a feature, you’ll likely call it a bug.
Some features of various software
To make my point clear, i have to introduce two features of software that are very practical for their anticipated use case and then change their context by adding another layer:
Ant filesets
If you use Ant as a build script language, you’ll find filesets very pratical. If you want to modify, copy or delete a bunch of files, you specify a root directory and some similarities between the files (like equal filetypes or names) and you’re done. Let me give you an example to show the use case:
<delete>
<fileset dir="${basedir}" include="**/build.xml,**/pom.xml"/>
</delete>
This will very likely delete all ant build scripts and maven setting files in your project (so please use with care). Notice how the include attribute is comma-separated for multiple patterns. According to the documentation, the comma can be omitted for a space character.
Then, there is Hudson, a very powerful continuous integration server. One source of its power is the familiarity of configuration syntax, specifically when accessing a bunch of files:
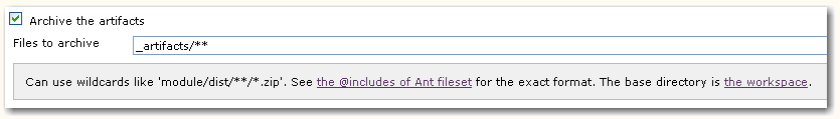
The given text field specifies the include attribute of an Ant fileset. You immediately inherit all the power of ant’s fileset, but the features, too. Here, it’s a feature that two pattern can be excluded by just a space character. If your path contains spaces, you cannot express your pattern in this text field. When using the fileset directly in Ant, you can alter the syntax and use multiple nested include tags, but within Hudson, you are stuck with the single include attribute.
Struts2 internationalization
The second example is fully described in my previous blog entry (“The perils of \u0027”).
As a short summary: The Struts2 framework inherits the power of Java’s MessageFormat when loading language dependent text. As the apostrophe is a special character to MessageFormat, it cannot be used directly in the text entries.
The principle behind the examples
Both examples share a common principle: “Stacked smartness doesn’t add up“. What’s a feature to one software, may be a bug to a software that builds on top of it.
Software developers tend to “stack up” different third party software products to compose their own product with even higher-level functionality. There is nothing wrong with this approach, as long as the context of the underlying products doesn’t change much. If it changes, features begin to behave like bugs.
The cost of stacking
Stacked products are likely to increase the ability of skilled users to re-use their knowledge. Every developer familiar to Ant will instantly be empowered to use the file patterns of Hudson. Every developer familiar to MessageFormat can produce powerful i18n entries that do most of the formatting automatically. That’s a great productivity gain.
But on the other side, if you aren’t familiar to ant when using hudson or know nothing about MessageFormat when just translating the i18n entries of a Struts2 webapp, you’ll be surprised by strange effects. And you won’t find sufficient documentation of these effects in the first place. There will be a link to some obscure project or class you never heard about, telling you all sorts of details you don’t want to hear right now. You can’t easily put them into the right context anyway. You will be down to trial and error, frustrated that your use case seems impossible without explanation. That’s a great productivity loss.
Often, you can’t blame any part of the stack, not even the topmost, for the occuring bugs. If a specific stack maintains and increases productivity, depends on the use case of the topmost layer compared to the underlying anticipated ones. If those aren’t documentated, its hard to notice the displacement.
A metaphor on software stacks
Whenever I hear about a software stack, a picture of a man on a stack of crates occurs to me. Here is the original photo of my thoughts.
What’s your encounter with a shaky stacking?